Introduction
In an era where mobile devices have become an extension of our lives, security is paramount. Biometric authentication has emerged as a promising solution to safeguard our personal information and data. However, is it truly the silver bullet for mobile device security, or does it come with its own set of risks and vulnerabilities? This article explores the world of biometric security in mobile devices and delves into the complexities that make it a double-edged sword.
The Rise of Biometric Authentication
Evolution of Mobile Security
Mobile devices have evolved from simple communication tools to multifunctional devices that store a wealth of personal and sensitive information. Consequently, securing these devices has become a top priority for both users and manufacturers.
The Biometric Revolution
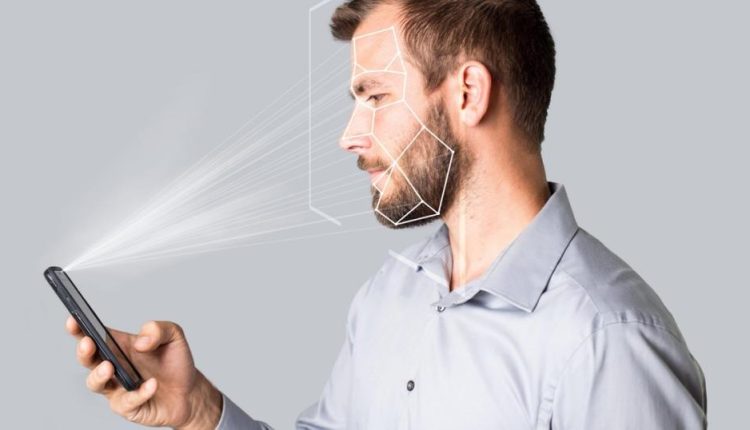
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and iris scanning, have gained prominence as they offer a more convenient and secure alternative to traditional PINs and passwords. Users can unlock their devices or authenticate transactions with a simple touch or glance, making the process seamless and efficient.
The Benefits of Biometric Security
Enhanced User Experience
Biometric authentication eliminates the need to remember complex passwords, reducing the risk of forgotten credentials and the hassle of frequent password resets. This enhances the overall user experience and encourages users to adopt stronger security measures.
Improved Security
Biometric data is unique to each individual, making it difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to a device. This increased security reduces the chances of unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft.
Convenience and Speed
Biometric authentication is incredibly convenient and quick. Users can access their devices or make secure transactions with a simple touch or glance, saving valuable time and effort.
The Dark Side of Biometric Security
Privacy Concerns
Collecting and storing biometric data raises significant privacy concerns. Users worry about the misuse of their biometric information, especially in the event of a data breach. Ensuring the secure storage and handling of biometric data is a critical challenge.
Vulnerabilities to Spoofing
Biometric systems are not foolproof. Facial recognition can be fooled with photos, fingerprint scanners with artificial fingerprints, and iris scanning with contact lenses. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers with the right tools and knowledge.
Legal and Ethical Issues
The legal and ethical aspects of biometric data collection and usage are complex. Regulations and laws governing biometric data differ from one region to another, making compliance a challenge for multinational corporations.
Striking a Balance
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
To mitigate the risks associated with biometric security, many experts recommend implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA combines biometrics with other authentication methods, such as PINs or one-time passwords, to add an extra layer of security.
Continuous Innovation
Manufacturers must stay ahead of attackers by continually innovating and improving biometric technology. This includes developing more advanced recognition algorithms and enhancing anti-spoofing measures.
Conclusion
Biometric security in mobile devices offers a tantalizing blend of convenience and enhanced security. However, it is not without its challenges and vulnerabilities. To make the most of this double-edged sword, users and manufacturers must strike a delicate balance between convenience and security. Biometric authentication is a valuable tool in our quest for mobile device security, but it should not be relied upon as the sole solution. By adopting a multi-faceted approach to security and remaining vigilant in the face of emerging threats, we can ensure that our mobile devices remain safe havens for our personal information and data.


Comments are closed.